A Santani Guest’s Experience
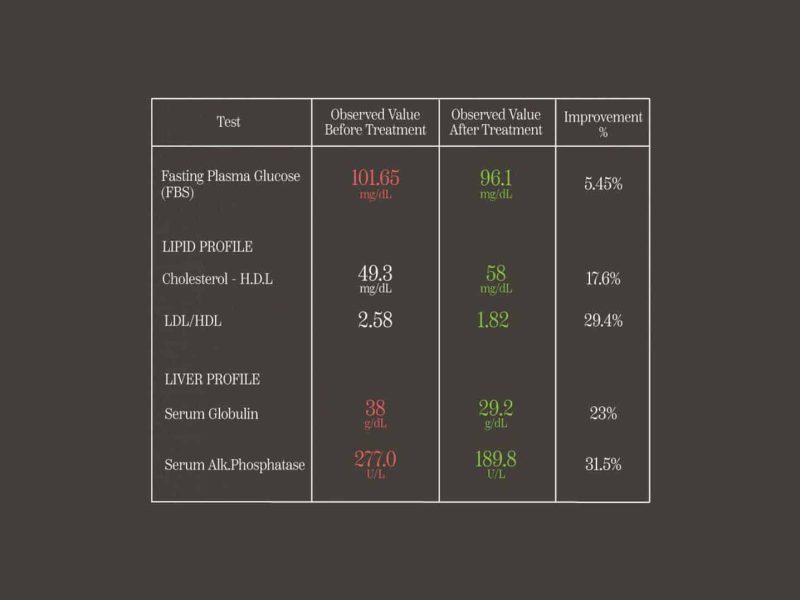
A guest at Santani came to us with blood reports (featured below) taken during a routine health checkup. It showed a slightly abnormal liver function. The doctors at the resort advised the guest to follow Santani detox retreat program for seven days. After just 7 days his lab reports showed incredible improvement in liver function by the reduction of all liver damage indicators. His lipid profile also showed better control following the detox program.
- His Fasting Plasma went down 5.45% from 101.65 mg/dL to 96.1 mg/dL.
- His Lipid Profile showed cholesterol H.D.L improve by 17.6% and LDL/HDL improve by 29.4%.
- His Liver Profile showed more incredible results as his serum globulin reduced 23% from 38 g/dL to 29.2 g/dL and his serum alk. phosphatase went down 31.5% from 277 U/L to 189.8 U/L.
Liver Disease
The liver is considered to be the largest glandular organ of the body and one of the most vital organs that functions as a centre for the metabolism of nutrients such as carbohydrates, proteins and lipids and the excretion of waste metabolites. It protects our body from various injurious substances and toxic metabolic byproducts by means of excretion. It also handles the metabolism and excretion of drugs and other xenobiotics from the body thereby providing protection against foreign substances by detoxifying and eliminating them. The bile secreted by the liver plays an important role in digestion that emulsifies fats and helps the absorption of vitamin K from the diet. Other functions of the liver are the production of clotting factors like fibrinogen, prothrombin, factor V, VII, VIII etc. and the production of red blood cells.
Despite tremendous scientific advancement in the field of hepatology in recent years, liver disease constitutes a major problem globally. There are more than a hundred well-known liver diseases with diversified etiopathology. The most frequent causes of hepatic disease include infectious agents (especially hepatitis viral A, B, and C), obesity-related fatty liver disease, xenobiotics (alcohol, drugs, and chemicals) induced liver injury, inherited and genetic defects related liver diseases, autoimmune hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and primary or secondary liver cancer. Jaundice and hepatitis are two major hepatic disorders that account for a high death rate.
Exposure of the liver to free radicals derived from xenobiotics leads to oxidative stress, which is recognized to be an important factor responsible for liver injury or be involved in the pathogenesis of a liver disorder. Most hepatotoxic chemicals damage liver cells by inducing lipid peroxidation and other oxidative damage. In the oxidation process, highly reactive and harmful chain reactions of oxygen species are generated, causing damage to living organisms. The oxygen centred free radicals and other reactive oxygen species (ROS), which are continuously produced, have resulted in cell death or tissue damage. This oxidation damage caused by free radicals is related to pathogenesis of many chronic degenerative diseases.
The liver profile measures a series of chemicals in relation to the way the liver works to check whether your liver is under strain, inflamed, infected or diseased. These tests can also show how well the treatment is working.
The most important liver test is the serum albumin test. This test is used to measure the level of albumin (a protein in the blood) which is produced by the liver and may be useful in the diagnosis of liver disease. A low level of albumin indicates the liver is not functioning properly. AST (aspartate aminotransferase) is an enzyme that is found mostly in the liver, but also in muscles and other organs in the body. When cells containing AST are damaged, they release the AST into the blood. ALT (alanine transaminase) is an enzyme found mostly in the liver. When liver cells are damaged, they release ALT into the bloodstream. A high result on an AST test might indicate a problem with your liver or muscles. Elevated AST without elevated ALT may indicate heart or muscle disease. ALP (Alkaline phosphatase) is an enzyme found in many parts of the body. But most ALP is found in the liver, bones, kidneys and digestive system. High ALP levels may indicate that there’s damage to your liver or that you have a type of bone disorder. Your blood can show higher levels of ALP if one of the bile ducts that drains your liver becomes blocked. Conditions such as liver cancer, cirrhosis, and hepatitis can also cause ALP levels to rise. If ALT, bilirubin, and ALP are also elevated, it indicates liver damage.
| Result | |||||
| Test | Before – Laboratory X | After – Laboratory Y | |||
| Observed Value | Reference Range | Result | Flag Reference Value | Comments | |
| Fasting Plasma Glucose (FBS) | 101.65 mg/dL | 96.1 mg/dL | 70.0 – 99.0 | Normal : 70 – 99 Impaired Tolerance : 100 – 125 Diabetes mellitus : >= 126 | |
| LIPID PROFILE | |||||
| Serum Total Cholesterol | 199.0 mg/dL | 187.5 mg/dL | 140.0 – 239.0 | Desirable : < 200 Borderline High : 200 – 239 High : > 240 | |
| Serum Triglycerides | 113.0 mg/dL | 118.2 mg/dL | 10.0 – 200.0 | Normal : < 150 Borderline : 150 – 199 High : 200 – 500 Very High : > 500 | |
| Cholesterol – H.D.L | 49.3 mg/dL | 58.0 mg/dL | 35.0 – 85.0 | Normal : 40 – 60 Desirable : > 60 | |
| Cholesterol – Non – H.D.L | NE | 129.5 mg/dL | 55.0 – 189.0 | ||
| Cholesterol – L.D.L | 127.10 mg/dL | 105.9 mg/dL | 75.0 – 159.0 | Desirable : < = 129 Borderline High : 129 – 160 High : > 160 | |
| Cholesterol – VLDL | 22.60 mg/dL | 7.0 – 35.0 | 23.6 mg/dL | 10.0 – 41.0 | |
| CHOL/HDL | 4.04 | 3.0 – 5.0 | 3.2 | 2.0 – 5.0 | |
| LDL/HDL | 2.58 | 1.82 | 0.01 – 3.30 | Optimal : < 2.5 High : > 2.5 | |
| LIVER PROFILE | |||||
| Serum Total Protein | 78.0 g/L | 64.0 – 86.0 | 73.0 g/L | 60.0 – 83.0 | |
| Serum Albumin | 40.0 g/L | 34.0 – 50.0 | 43.8 g/L | 35.0 – 50.0 | |
| Serum Globulin | 38 g/dL | 23.0 – 37.0 | 29.2 g/L | 25.0 – 35.0 | |
| A/G Ratio | 1.05 | 0.8 – 2.3 | 1.5 | 0.8 – 2.3 | |
| Serum Bilirubin – Total | 0.82 mg/dL | 0.1 – 1.2 | 0.57 mg/dL | 0.1 – 1.2 | |
| Serum Alk.Phosphatase | 277.0 U/L | 46 – 116 | 189.8 U/L | 100.0 – 290.0 | |
| Serum ALT (S.G.P.T) | 44.0 U/L | 0.0 – 40.0 | 32.2 U/L | 0.1 – 40.0 | |
| Serum AST (S.G.O.T) | 25.0 U/L | 0.0 – 40.0 | 19.6 U/L | 0.1 – 40.0 | |
| Serum Gamma – GT | 53.0 U/L | 15.0 – 85.0 | 38.8 U/L | 0.1 – 49.0 | |